By Sally Westwood
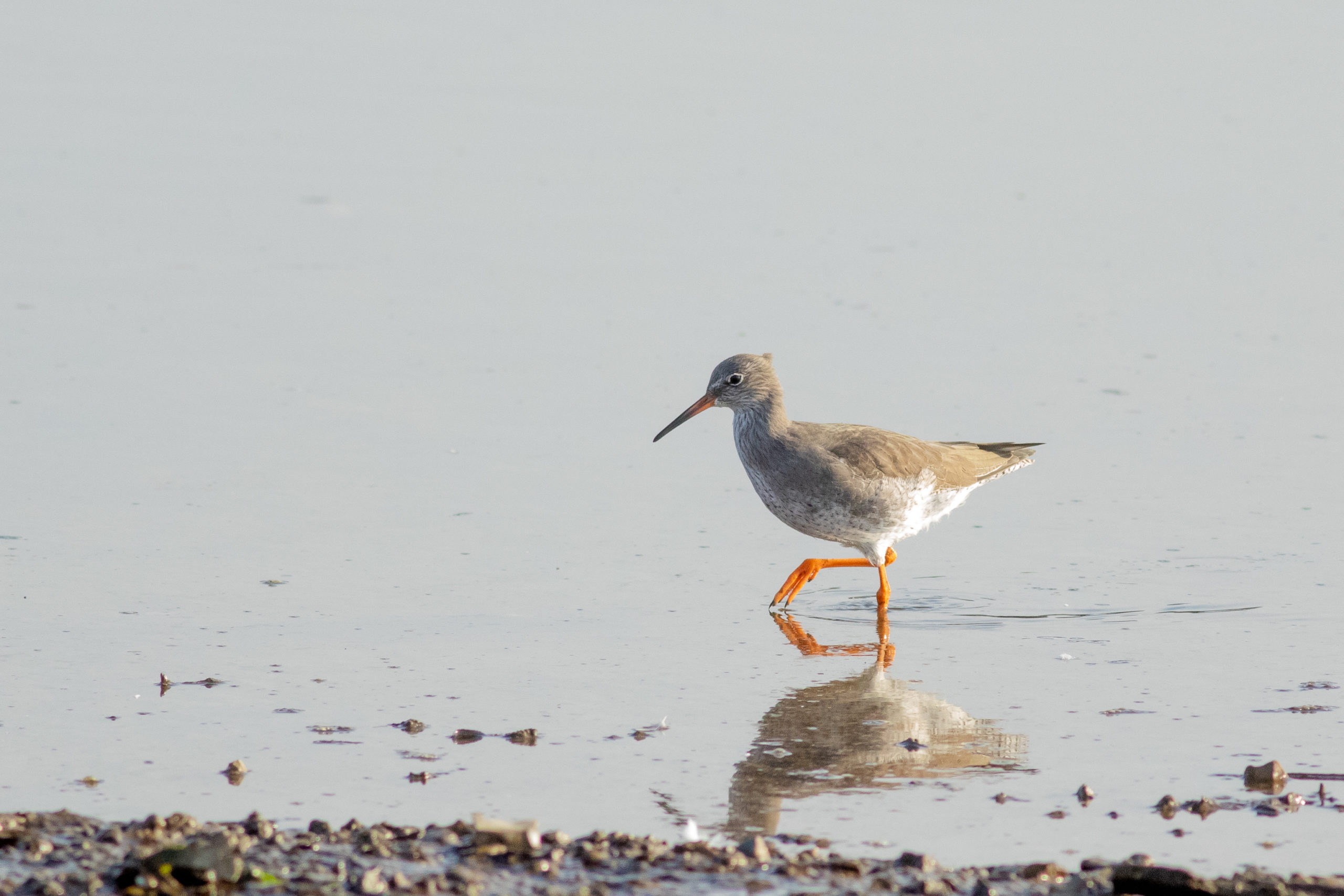
In 2021, Suffolk Coast & Heath Area of Natural Beauty (AONB) selected the Redshank1 as their flagship bird as a part of their Nature Recovery Plan2. Commendably, they called for volunteers to help with the project of protecting the Redshank including their nesting habitat. Redshanks are present on the River Deben but I have only ever seen one feeding along the river’s edge, on my river walk. I thought it might be interesting for the reader to have some insight on the background of Suffolk Coast & Heath AONB’s Nature Recovery intervention and the plight not only of the Redshank, but as we might have suspected, a considerable number of species of birds, that visit the Deben. It is not a comfortable read, however, the good news is, steps are being taken to stop the decline in species.