by Sally Westwood

Curlew (Numenius arquata)
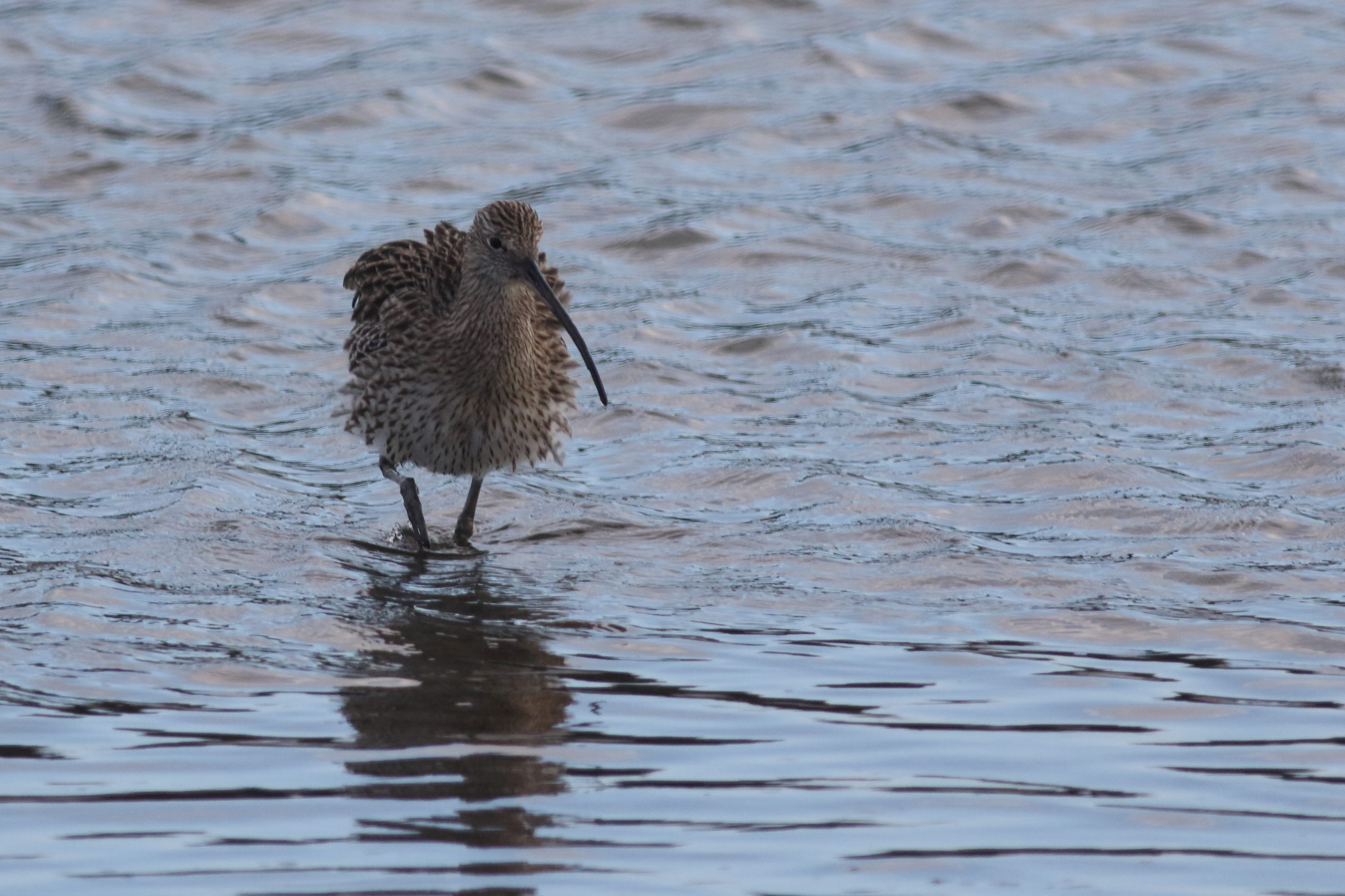
The tide was ebbing, almost at low tide, it was about an hour before sunset. The Deben was embellished with a clear, magical light that appears just before sunset and sunrise. Such a light produces enhanced clarity of detail in everything visible to the eye. Two Curlews1 landed on the mudflat, one each side of a gully of water draining into the shallow channel of the river. Curlews are the largest waders in the UK, with a streaked and barred plumage, long legs and a distinctive down curved bill2, see image above. In flight, it shows a white section on the rump. The Whimbrel3 by comparison, is a similar bird to the Curlew, except it has a shorter, thicker bill, with a narrow stripe on the crown and is smaller than the Curlew, see image below. In flight, it shows a white section on the tail and back. I was alerted to the Curlew’s presence from their distinctive “Curlew, Curlew’’ calls made when they were flying. It is a call I regard as haunting in the cold, overcast days of winter. They also have a trembling, evocative bubbling call, that ends with what may be described as “dude” which carries some distance. One Curlew joined the other, on the other side of the gully. They immediately started squabbling, poking their long slender, down curved bills at each other, raising their wings slightly. Moments later, the set too ended when one returned to the other side of the gully and started searching for food, poking its bill, deep into the mud. The other Curlew started bathing and shaking out feathers, as in the image above. They may have been a pair, or an adult and youngster, however, research on Curlews has indicated that the latter relationship may be unlikely4. Since Curlews in England and Wales are in decline and such decline is driven by factors occurring during the annual breeding season.
Continue reading →